Forklift Classification Chart: Forklifts are one of the most powerful vehicles for builders. Whether you need to move heavy loads in a warehouse or construction field, forklifts can safely lift objects humans cannot, making them indispensable on any job site.
Since there is a wide selection of styles and models, it can be difficult to select a forklift. Whether you’re looking to rent a forklift for your next project or purchase one, our guide covers the different forklift types, the benefits of each equipment, and popular forklift models to help choose the right forklift for your needs.

Forklift classifications
What are the different Forklift types?
Productivity and efficiency can be increased in the workplace if one chooses the correct equipment for his or her needs. Today, warehouse operators and fleet managers have a wide array of material handling equipment to choose from. Some of the popular options include aerial lifts, electric forklifts, LPG forklifts, pallet jacks, side loaders, and even automated guided vehicles (or AGVs). (Forklift Classification Chart)

If you are looking to get new equipment to accomplish key tasks more efficiently, it is recommended that you familiarize yourself with the forklift classifications set by OSHA (Occupational Safety and Health Administration). Below is a detailed look at forklift classifications Classes I through VII, including their key features and benefits:
- Class I: Electric motor rider trucks
- Class II: Electric motor narrow aisle trucks
- Class III: Electric pallet jack
- Class IV: Cushion tire forklift
- Class V: Solid pneumatic tires
- Class VI: Electric forklift truck
- Class VII: Rough Terrain Forklifts
Electric motor rider trucks
Class I Forklift Classification Chart are electric motor riders. These electric-powered forklifts are ideal for loading and unloading tractor-trailers, handling pallets, and a number of other applications in industries ranging from food storage and retail to factory and general warehousing.
Because they are powered by an electric battery, Class I forklifts are much quieter and create no emissions, making them a popular choice for indoor applications. Batteries on Class I forklifts also function as part of the counterweight to help maintain lifting capacity.

Electric motor narrow aisle trucks
Class II Forklift Classification Chart is electric, narrow aisle models. As the name suggests, Class II forklifts are designed with maneuverability that allows them to operate in tight spaces and narrow aisles. This class of forklifts is perfect for picking and putting away inventory, and these trucks provide users the ability to increase racking space without expanding their current warehouse.
Toyota offers two Class II forklift models, and you can explore the unique features of each by clicking on the model name from the list below.

Electric pallet jack
Class III Forklift Classification Chart equipment includes electric pallet jacks, stackers, and tow tractors. This class of equipment comes in both rider and walk behind (“walkie”) models, perfect for unloading deliveries and moving loads to a staging area where they can be handled by other types of forklifts.
Toyota offers 10 Class III models, including three different stackers that are ideal for food and beverage storage industries, among others. Click on each forklift model below to learn more.

Cushion tire forklift
Class IV Forklift Classification Chart are internal combustion engine cushion tire trucks. This class of sit-down forklifts is designed for indoor use. Class IV forklifts are powered by internal combustion (IC) engines that run on diesel fuel, LP gas, gasoline, or compressed natural gas. Their solid, cushioned tires provide a smooth ride on indoor surfaces and they’re puncture-proof since they are not air-filled.
These forklifts offer users outstanding versatility for warehousing, distribution, retail, and automotive applications.

Solid pneumatic tires
Class V Forklift Classification Chart are internal combustion engine pneumatic tire trucks. Forklifts in this class are similar to those in Class IV but are designed primarily for outdoor use. These forklifts are highly durable and are ideal for lumberyards, construction sites, and other outdoor applications.

Electric forklift truck
Class VI Forklift Classification Chart equipment includes electric and internal combustion engine tow tractors. These machines are most commonly used for towing loads rather than lifting. Trucks in this class are ideal for use at airports but are also commonly used in assembly line areas.

Rough Terrain Forklifts
Class VII forklifts are rough terrain trucks. Trucks in this class feature large, tractor-style tires and are powered almost exclusively by diesel engines for outdoor use in rugged terrain. Class VII trucks are most commonly used at lumberyards or construction sites to lift building materials to elevated work sites.

Forklift Classification Chart
How to Choose A Forklift: Forklift Classification Chart
To choose a forklift from all the different types, you’ll need to think about how the machinery will be used. Here are general criteria to reference when choosing a forklift to make sure your selected equipment performs efficiently and safely:
- Determine the capacity. How much weight do you need to lift?
- Calculate the weight of your job site. Can the ground sustain the forklift?
- Measure the height of the space. Can your forklift pass through openings?
- Select the correct fuel type. Do you need battery power or gas?
- Analyze the terrain. Is the surface smooth or uneven?
Forklift types vary in several aspects, from their fuel type and tire composition to their lift capacity and height. It’s important to consider these different factors when selecting a forklift. With their ability to lift and transport things of various sizes, forklifts are valuable players on any job site.
Hoisting and Rigging
Forklift Classification Chart
Hoisting and rigging (H&R) refers to the lifting and moving of loads using mechanical devices. The objectives of the hoisting and rigging program are to protect personnel from injury, the environment from harm, and equipment and property from damage; specifically, to protect load operators and others in the work area, scientific equipment, other government property, and the hoisting and rigging equipment itself.
Hoisting and rigging is a complicated topic and can have significant safety consequences if not performed correctly. Fundamental to the H&R program, and consistent with Your Company’s integrated safety and environment management system, is the expectation that organizations involved in hoisting and rigging activities take responsibility to understand the hoisting and rigging requirements and apply them to their operations.
Forklift classification types
The most popular forklift types on the market today are:
-Warehouse Forklift.
-Side Loader.
-Counterbalance Forklift.
-Telehandler.
-Industrial Forklift.
-Rough Terrain Forklift.
-Pallet Jack.
-Walkie Stacker.
Stand-up Reach forklifts are the most common variety and are mostly used when dispatching single loads into one bay. Alternatively, you can use a double-deep reach forklift, whose longer forks allow you to access bays with multiple pallet loads, as they will reach all the way to the back of the bay.
A forklift (also called lift truck, jitney, fork truck, fork hoist, and forklift truck) is a powered industrial truck used to lift and move materials over short distances.
Internal combustion engine used in a forklift. Forklifts powered by internal combustion engines run on a variety of fuels, including gasoline, diesel fuel, liquid petroleum gas (LPG), and compressed natural gas.
The most read

7 classes of forklifts
Fork crane models for industrial use within warehouses, hydraulic three-wheeled electric forklifts, etc.

Powered Industrial Truck Types
Commonly called forklifts or lift trucks are used in many industries, primarily to move materials.
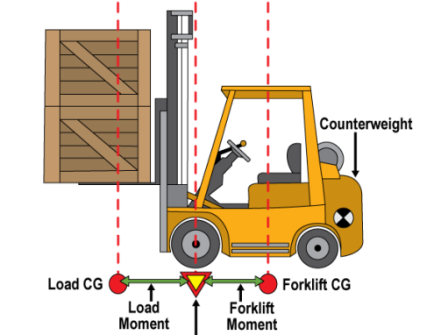
Forklift Capacity Calculator
The capacity factor is important in your selection regardless of whether you are buying the truck with the attachment or are adding the attachment to a truck yourself.

Forklift Safety Procedures
Forklifts are extremely useful workplace vehicles, as long as they are used safely and appropriately by operators who are appropriately trained and competent to use them.
