The urgent need to know the amount of oxygen in the body when you have a respiratory problem. Blood gas measurements provide critical information on oxygenation, ventilation, and acid-base status.
However, these measurements only provide a snapshot of the patient’s condition taken at the time the blood sample was drawn.
It is well known that oxygenation can change very quickly. In the absence of continuous monitoring of oxygenation, these changes may go unnoticed until it is too late.
Pulse oximeters measure oxygen saturation in the blood non-invasively and continuously, and can be done from home.
Pulse oximetry is a useful non-invasive tool in the evaluation of a patient with suspected hypoxia, few medical and nursing articles explain how to use this tool correctly.
This article reviews the basic physics of the pulse oximeter machine and proper use of the oximeter.
Limitations and sources of error in pulse oximeter technology are also outlined. Finally, the correct interpretation and application of the information obtained by pulse oximetry is explained.
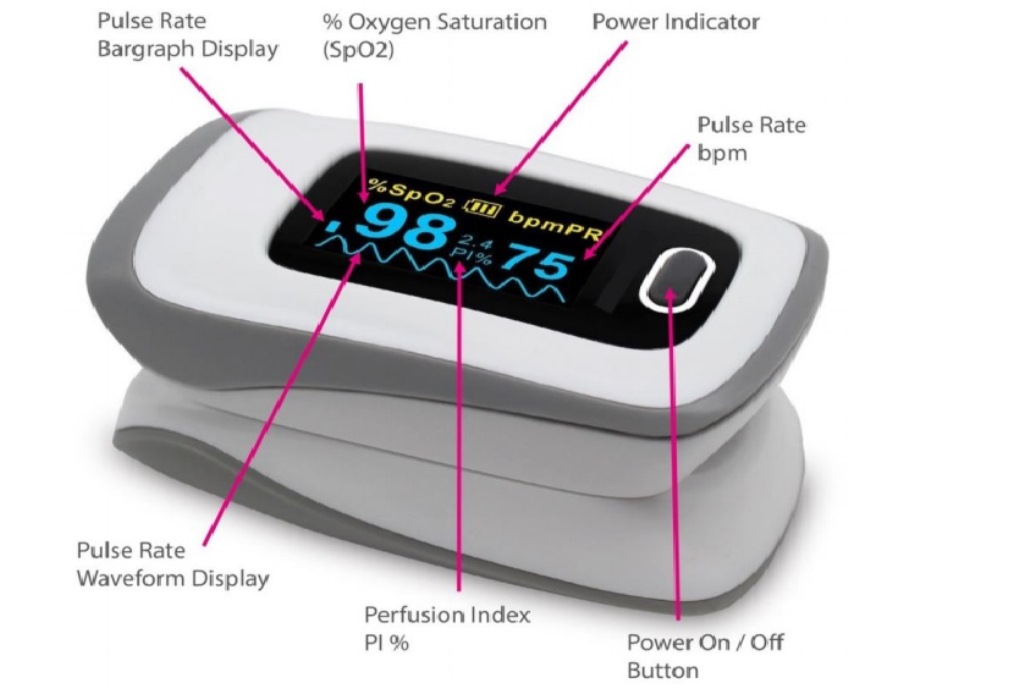
What are the 2 readings on a pulse oximeter?
A finger pulse oximeter measures two things:
- Blood Oxygen Saturation (SpO2): The measurement that indicates what percentage of blood is saturated, and
- Pulse Rate: Pulse rate is nothing but the heart rate that indicates the number of times a heart beats per minute.
Pulse oximeter readings normal range
The blood oxygen level measured with a fingertip pulse oximeter is called your oxygen saturation level (SpO2).
This is a percentage of how much oxygen your blood is carrying compared to the maximum it is capable of carrying.
Normally, more than 90% of your red blood should be carrying oxygen.
What is SpO2?
A blood-oxygen saturation reading indicates the percentage of hemoglobin molecules in the arterial blood which are saturated with oxygen.
The reading may be referred to as SaO2. Readings vary from 0 to 100%. Normal readings in a healthy adult, however, range from 94% to 100%.
The term SpO2 means the SaO2 measurement determined by pulse oximetry.
How Does Pulse Oximetry Work?
Within the Sp02 sensor, light-emitting diodes shine red and infrared light through the tissue. Most sensors work on extremities such as a finger, toe, or ear.
The blood, tissue, and bone at the application site absorb much of the light. However, some light passes through the extremity. A light-sensitive detector opposite the light source receives it.
Spo2 reading in oximeter
The oximeter may detect a pulse but is unable to measure SpO2 due to the pigment blocking the signal.
To recognize the settings in which pulse oximeter readings of oxygen saturation (SpO2) may result in false estimates of the true SaO2, an understanding of two basic principles of pulse oximetry is required:
- how oxyhemoglobin is distinguished from deoxyhemoglobin, and
- how the SpO2 is calculated only from the arterial compartment of blood.
The ability of pulse oximetry to detect SpO2 of only arterial blood is based on the principle that the amount of red and IR light absorbed fluctuates with the cardiac cycle, as the arterial blood volume increases during systole and decreases during diastole; in contrast, the blood volume in the veins and capillaries as well as the volumes of skin, fat, bone, etc, remain relatively constant.
SpO2 Sensors
Most sensors work on extremities such as a finger, toe, or ear.
The sensor measures the amount of red and infrared light received by the detector and calculates the amount absorbed.
Much of it is absorbed by tissue, bone, and venous blood, but these amounts do not change dramatically over short periods of time.
The amount of arterial blood does change over short periods of time due to pulsation (although there is some constant level of arterial blood).
Because the arterial blood is usually the only light-absorbing component that is changing over short periods of time, it can be isolated from the other components.
Absorption at the Sensor Site
The amount of light received by the detector indicates the amount of oxygen bound to the hemoglobin in the blood. Oxygenated hemoglobin absorbs more infrared light than red light.
Deoxygenated hemoglobin absorbs more red light than infrared light. By comparing the amounts of red and infrared light received, the instrument can calculate the SpO2 reading
How can use pulse oximeter?
Common Areas for Use of Pulse Oximetry
- During anesthesia and postanesthesia care.
- Intensive care units
- Neonatal care units
- Nursery, and neonatal intensive care unit
- Hospital medical units
- Transportation within the hospital and during ambulance or air ambulance transportation
- Diagnostic testing, such as pulmonary function testing, exercise testing, and during sleep studies
- Subacute care centers, such as nursing homes and rehabilitation centers
- Home care patients
How to read a pulse oximeter?
Pulse oximetry is an objective measure of oxygenation and is simple, reliable, and accurate when used appropriately.
Pulse oximetry is a useful tool in assessing the oxygenation status of a patient and can be used routinely in many areas of clinical practice.
Through the use of pulse oximetry, oxygenation can be controlled in a simple and non-invasive way. Advances in microprocessor technology, along with improvements in light-emitting diodes and photoelectric sensors, have improved the accuracy and reliability of pulse oximetry.
However, due to the inherent limitations of non-invasive technology, it is important to know how to interpret the information received from oximetry.
Pulse oximetry has gained wide clinical acceptance in many areas. Small portable systems are available for use almost anywhere.
Almost all patients requiring oxygen or mechanical ventilation would benefit from clinical monitoring of their oxygen status by pulse oximetry, which can be in the form of continuous monitoring or by intermittent testing.
Oxygen saturation calculated by pulse oximetry has a 95% confidence rate of ± 4%, so oximetry is considered reliable on readings ranging from 70% to 100% SpO2.
.
This means that, although pulse oximetry is not a substitute for blood gas testing, it can be used as a screening tool when poor oxygen saturation is suspected.

FDA approved Oximeter made in the USA
-Ever wonder if there are pulse oximeters made in the USA?
-How many medical device manufacturers are there in the United States?

What are the 2 readings on a pulse oximeter?
A finger pulse oximeter measures two things:
-Blood Oxygen Saturation
-Pulse Rate
